#라이브러리 없이 코딩하기
구현 알고리즘
-
Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
다음번에 시도해 보기
-
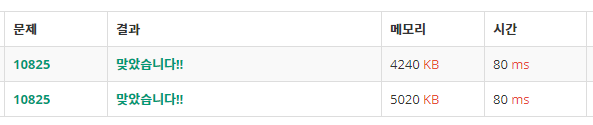
퀵소트로 구현하면 시간을 더 단축시킬 수 있는 문제인 것 같으니 도전해보기 (머지소트 실행시간 : 80ms)
+ 퀵소트는 시간을 단축시키지는 않았지만, 머지소트에 사용되는 포인터 어레이 만큼의 메모리 사용량을 줄일 수 있었다.
(아래 : merge sort, 위 : quick sort)
소스 코드 (merge sort)
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_NODE 100001
struct Node {
char name[11];
int korean, english, math;
} nodes[MAX_NODE], *nt[MAX_NODE], *tmp[MAX_NODE];
void mstrcpy(char* dst, const char* src) {
while(*src) {
*dst++ = *src++;
}
*dst = '\0';
}
int mstrcmp(const char* a, const char* b) {
while (*a && *a == *b) {
++a; ++b;
}
return *b - *a;
}
int cmpScore(Node *n1, Node *n2) {
if (n1->korean != n2->korean)
return n1->korean - n2->korean;
if (n1->english != n2->english)
return n2->english - n1->english;
if (n1->math != n2->math)
return n1->math - n2->math;
return mstrcmp(n1->name, n2->name);
}
void mergeSort(int start, int end) {
if (start < end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
mergeSort(start, mid);
mergeSort(mid + 1, end);
int s1 = start;
int s2 = mid + 1;
int idx = start;
while (s1 <= mid && s2 <= end) {
if (cmpScore(nt[s1], nt[s2]) > 0)
tmp[idx++] = nt[s1++];
else
tmp[idx++] = nt[s2++];
}
while (s1 <= mid) tmp[idx++] = nt[s1++];
while (s2 <= end) tmp[idx++] = nt[s2++];
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
nt[i] = tmp[i];
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
char name[11];
int a, b, c;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%s %d %d %d", name, &a, &b, &c);
Node* newN = &nodes[i];
mstrcpy(newN->name, name);
newN->korean = a;
newN->english = b;
newN->math = c;
nt[i] = newN;
}
mergeSort(0, n-1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%s\n", nt[i]->name);
}
}
소스코드 (quick sort)
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_NODE 100001
struct Node {
char name[11];
int korean, english, math;
} nodes[MAX_NODE], * nt[MAX_NODE];
void mstrcpy(char* dst, const char* src) {
while(*src) {
*dst++ = *src++;
}
*dst = '\0';
}
int mstrcmp(const char* a, const char* b) {
while (*a && *a == *b) {
++a; ++b;
}
return *b - *a;
}
int cmpScore(Node *n1, Node *n2) {
if (n1->korean != n2->korean)
return n1->korean - n2->korean;
if (n1->english != n2->english)
return n2->english - n1->english;
if (n1->math != n2->math)
return n1->math - n2->math;
return mstrcmp(n1->name, n2->name);
}
void quickSort(int start, int end) {
if (start >= end) return;
int pivot = start;
int i = pivot + 1;
int j = end;
Node* tmp;
while (i <= j) {
while (i <= end && cmpScore(nt[i], nt[pivot]) > 0)
i++;
while (j > start && cmpScore(nt[j], nt[pivot]) < 0)
j--;
if (i > j) {
tmp = nt[j];
nt[j] = nt[pivot];
nt[pivot] = tmp;
}
else {
tmp = nt[i];
nt[i] = nt[j];
nt[j] = tmp;
}
}
quickSort(start, j - 1);
quickSort(j + 1, end);
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
char name[11];
int a, b, c;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%s %d %d %d", name, &a, &b, &c);
Node* newN = &nodes[i];
mstrcpy(newN->name, name);
newN->korean = a;
newN->english = b;
newN->math = c;
nt[i] = newN;
}
//mergeSort(0, n-1);
quickSort(0, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%s\n", nt[i]->name);
}
}'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 백준 1764번 - 듣보잡 (0) | 2021.03.11 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] 백준 7785번 - 회사에 있는 사람 (0) | 2021.03.11 |
| [알고리즘] 백준 1620번 - 나는야 포켓몬 마스터 이다솜 (0) | 2021.03.11 |
| [LeetCode] 1. Two Sum _Python 딕셔너리 (0) | 2021.01.19 |
